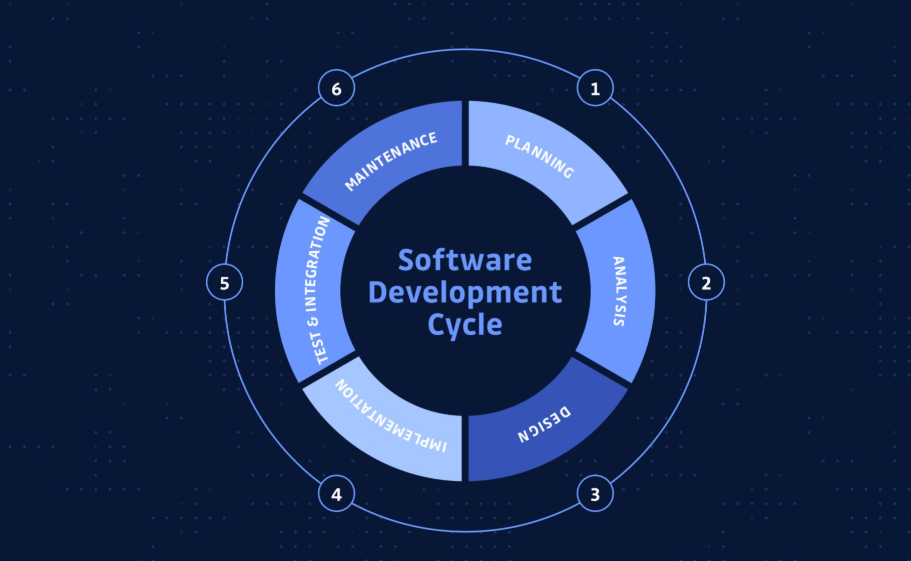
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) serves as a critical framework for guiding software projects from inception to completion. It emphasizes structured phases such as planning, design, development, and testing, ensuring that each step is strategically aligned with user needs. Collaboration among stakeholders is vital throughout this process. Understanding these phases can reveal how effective management of the SDLC not only enhances product quality but also fosters innovation. What implications does this have for the future of software development?
Planning and Requirements Gathering
In the foundational phase of the Software Development Life Cycle, Planning and Requirements Gathering serves as a critical blueprint for project success.
This stage emphasizes stakeholder involvement, ensuring that diverse perspectives shape the vision. Through rigorous requirement analysis, teams identify essential functionalities, aligning project goals with user needs.
Collaborative discussions foster clarity, paving the way for a development process that champions freedom and innovation.
See also: The Social Impact of Rapid Technological Growth
Design and Prototyping
The design and prototyping phase stands as a pivotal juncture in the Software Development Life Cycle, where concepts evolve into tangible representations.
This stage emphasizes crafting the user interface and enhancing user experience through iterative feedback and collaboration.
Strategic decisions made here shape functionality and aesthetics, ultimately fostering an environment that champions innovation, ensuring that the final product resonates with user needs and aspirations.
Development and Implementation
Development and implementation mark the transition from design concepts to functional software, where developers translate intricate designs into robust code.
This phase emphasizes code optimization and collaborative efforts to incorporate feature enhancements, ensuring that the software meets user needs.
Testing and Deployment
As the software nears completion, testing and deployment become critical phases that ensure the product’s reliability and performance.
Automated testing plays a vital role in identifying bugs and validating functionality, while strategic deployment strategies facilitate seamless delivery to users.
Collaboration among developers, testers, and stakeholders enhances the process, fostering a shared commitment to quality and user satisfaction, ultimately granting users the freedom to innovate.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) serves as a vital framework for producing high-quality software that meets user needs. Remarkably, organizations that adhere to a structured SDLC approach experience up to 30% fewer project failures compared to those that do not. This statistic underscores the importance of meticulous planning, collaborative design, and thorough testing. By embracing the SDLC, teams can foster innovation and ensure continuous improvement, ultimately enhancing user satisfaction and project success.